18.04.2019
Why hormonal? Women's secrets or why it is so important to know about hormones
It is known that all processes in our body are controlled by hormones. Mood, health, appearance, appetite, sleep, intelligence - this, and much more, depends on hormones.
estrogen
One of the most famous female hormones is estrogen, which is produced in the ovaries. This is a sex hormone due to which a woman has female figure And female character. The roundness of the figure, a soft, compliant character, emotionality - we have all this due to the production of the hormone estrogen in the body.
Besides, it is able to accelerate the renewal of cells throughout the body, maintain youthful shine and health of hair and skin, and also protects blood vessels from cholesterol deposits.
It is clear that the hormone must be produced in the required quantity.
 Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: estrogen
Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: estrogen
Excess estrogen may cause excessive fullness in the lower abdomen and thigh area. In addition, doctors associate various benign tumors with an excess of this female hormone.
Its disadvantage often causes increased hair growth in unwanted places: on the face, legs, arms.
In case of a lack of this hormone, a woman ages faster: the skin is more prone to wrinkles and fading, hair becomes dull and lifeless, etc.
Female hormone: testosterone
In women, the hormone testosterone is produced in the adrenal glands.
 Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: testosterone
Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: testosterone
Its excess often turns a woman into an ardent lover of men. Thanks to testosterone, we can experience sexual desire, be purposeful and persistent.
This hormone can force a woman not only to fold her arms in anticipation of a man, but also to go hunting for him herself.
The more testosterone a woman produces, the easier and faster it is for her to build her muscles and get involved in active games. With an excess of the hormone, a woman becomes aggressive and hot-tempered.
If the body does not produce enough testosterone, then the woman does not want to have sexual relations at all.
Female hormone: oxytocin
The female hormone oxytocin is a hormone that forces us to be tender and affectionate. IN large quantities Oxytocin is produced after childbirth. This explains our boundless love for the tiny creature that was born.
 Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: oxytocin
Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: oxytocin
This hormone is produced in large quantities during stress. That is why a woman tries to get rid of depression and anxiety by taking care of her children, her husband, and doing good deeds.
Female hormone: thyroxine
Thyroxine is a hormone that affects our mind and figure. It regulates metabolism. The faster it happens, the more difficult it is for a woman to gain weight and, vice versa.
In addition, thyroxine affects our intelligence. Thanks to this hormone, a woman can have a slim figure, smooth skin and graceful movements. Interestingly, it is thyroxine that allows a woman to instantly respond to an interested male gaze. The hormone is synthesized in the thyroid gland.
Excess and deficiency of the female hormone: thyroxine
If the body produces thyroxine in excess, the woman loses weight very quickly. In addition, she has difficulty concentrating. One thought constantly replaces another, the woman experiences constant anxiety, suffers from insomnia, and her heart jumps out of her chest. A deficiency of this hormone causes drowsiness, lethargy and obesity, as well as memory impairment. 
Female hormone: norepinephrine
Norepinephrine is called the hormone of rage and courage. During a stressful situation, this hormone is produced in the adrenal glands. Many people know the opposite hormone to this - the fear hormone, which makes us run away from danger. Norepinephrine, on the contrary, awakens in a woman a feeling of confidence and readiness for action.
The hormone dilates blood vessels, blood rushes to the head, and brilliant ideas come to our minds, our cheeks become rosy, wrinkles are smoothed out, and our eyes sparkle with bright fire. Norepinephrine helps a woman with her head held high to solve all problems, find ways out of troubles and look great at the same time.
Many men will not let you lie that sometimes during times of stress, a woman does not fade, but, on the contrary, only blossoms.
There is no feeling of anxiety or insomnia. Very often you can observe that the slightest trouble takes us out of balance and makes us feel depressed. And sometimes nothing can piss us off! Thanks to the hormone norepinephrine!
Female hormone: insulin
 Insulin is commonly called the “sweet life” hormone. It enters the bloodstream from the pancreas and controls blood glucose levels. Insulin breaks down all incoming carbohydrates, incl. sweets, and processes them into glucose (a source of energy). That. Insulin gives us the energy that allows us to live.
Insulin is commonly called the “sweet life” hormone. It enters the bloodstream from the pancreas and controls blood glucose levels. Insulin breaks down all incoming carbohydrates, incl. sweets, and processes them into glucose (a source of energy). That. Insulin gives us the energy that allows us to live.
Some women produce slightly less insulin from birth, than others, or the hormone is not as active.
When we eat too much sweet or starchy foods, excess glucose “wanders” throughout the body and negatively affects the condition of cells and blood vessels. As a result, diabetes may develop. The risk is especially high if members of your family suffer from this disease.
Female hormone: somatotropin
This female hormone is responsible for strength and slimness. The hormone is produced in the pituitary gland, an endocrine gland located in the brain. Somatotropin is responsible for burning fat, building muscle mass, strength and elasticity of ligaments, incl. and those that support the female breast.
In childhood and adolescence, an excess of this hormone leads to very high growth. If this hormone is produced in excess in an adult body, what can still grow grows: the chin, nose, knuckles. Excessive amounts of the hormone during pregnancy can lead to enlargement of some facial features, hands, feet, and hands, but after the birth of the baby, everything usually falls into place. In children, a lack of growth hormone is fraught with a slowdown, and often a complete stop of growth.
 If a woman constantly does not get enough sleep, often overeats and is overtired, the level of the somatotropin hormone decreases, the muscles become weak, flabby, and the breasts lose their shape. However, no amount of intensive training will correct the situation.
If a woman constantly does not get enough sleep, often overeats and is overtired, the level of the somatotropin hormone decreases, the muscles become weak, flabby, and the breasts lose their shape. However, no amount of intensive training will correct the situation.
Hormones control all processes in the female body. Reception hormonal drugs can lead to hormonal imbalance, and the results of such treatment can be the most unexpected!
Therefore, before you start taking them, you need to assess the existing risk.
Knowing your hormonal levels is just as important for a woman as monitoring your weight, blood pressure and hemoglobin. Your hormone levels determine how you look and feel. Let's take a closer look at the role hormones play in a woman's body.What are hormones?
Hormones are organic substances with high physiological activity, designed to control the functions and regulate the main systems of the body. They are secreted by the endocrine glands and released into the bloodstream of the body and travel through the bloodstream to their “destination”, namely to the organs to which its action is directly directed. The same hormone can have several organs to which its action is directed.A healthy body must have hormonal balance throughout endocrine system in general (between the endocrine glands, the nervous system and the organs on which the action of hormones is directed). If the functioning of one of the components of the endocrine system is disrupted, the functioning of the entire body, including the reproductive system, changes, therefore, the ability to conceive is reduced.
More about hormones
Estrogen produced in the ovaries. Until adolescence, this hormone is secreted in small quantities. With the onset of puberty, there is a sharp jump in estrogen production - girls develop breasts and their figure takes on a pleasant, rounded shape. Estrogen accelerates the process of cell renewal in the body, reduces the secretion of sebum, maintains elasticity and youthfulness of the skin, and gives shine and volume to our hair. Among other things, this hormone, important for the female body, protects blood vessels from the deposits of cholesterol plaques, and, therefore, prevents the development of atherosclerosis.Excess estrogen can cause excessive fullness in the lower abdomen and thighs. In addition, doctors associate various benign tumors with an excess of this female hormone.
Its deficiency often causes increased hair growth in unwanted places: on the face, legs, arms. If there is a lack of this hormone, a woman ages faster: the skin is more prone to wrinkles and fading, hair becomes dull and lifeless, etc.
This hormone is given on the 3-7th (depending on the purpose of the study) day of the cycle. The study is carried out on an empty stomach.
Estradiol- has an effect on all female organs, promotes the development of secondary sexual characteristics: the formation of mammary glands, the distribution of subcutaneous fat, the appearance of libido. Its role is especially important in the development of the uterine mucosa and its preparation for pregnancy - the growth of the functional layer of the uterus, which reaches its maximum thickness by the middle of the cycle. This hormone is secreted by the maturing follicle, corpus luteum of the ovary, adrenal glands and even adipose tissue under the influence of FSH, LH and prolactin. In women, estradiol ensures the formation and regulation of menstrual function and the development of the egg. Ovulation occurs 24-36 hours after a significant peak in estradiol. After ovulation, the hormone level decreases, and a second, smaller amplitude, rise occurs. Then there is a decline in the concentration of the hormone, which continues until the end of the luteal phase. Estradiol is responsible for the accumulation of fat in the female body, including during pregnancy.
Insufficient production of estradiol in a woman of childbearing age can manifest itself as hot flashes, autonomic disorders, and increased blood pressure, as happens during physiological menopause. In addition, a lack of this hormone threatens excessive growth of male-pattern hair, deepening of the voice, and absence of menstruation.
However, an excess of estradiol is a bad sign. A sharp increase in estrogen can lead to the formation of tumor processes in the organs of a woman’s reproductive system. That is why regular monitoring of this hormone is necessary, and you can take it throughout hormonal cycle depending on medical indications.
Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) regulates the activity of the gonads: promotes the formation and maturation of germ cells (eggs and sperm), affects the synthesis of female sex hormones (estrogens). If there is a deficiency in the production of this hormone, then diseases of the pituitary gland and inability to conceive are noted.
The maximum concentration of FSH is observed in the middle of the cycle, which leads to ovulation. This hormone is given on the 2-8th (depending on the purpose of the study) day of the cycle. At the same time, to determine the growth of the follicle, it is more advisable to take this hormone on days 5-7 of the cycle. The study is carried out on an empty stomach. 3 days before the study you need to exclude strong physical exercise, within 1 hour before it - smoking and emotional stress.
Luteinizing hormone (LH)- ensures the completion of the process of maturation of the egg in the follicle and ovulation (the release of a mature female egg from the ovary), the formation of the “corpus luteum” with the secretion of the hormone progesterone.
Luteinizing hormone (LH) is given in the same way as FSH on days 3-8 menstrual cycle. The study is carried out on an empty stomach.
Progesterone- this hormone is involved in the maturation and preparation of the uterus for pregnancy; under its influence, the mucous membrane of the uterus “looses” and “moisturizes.” In general, progesterone is the “hormone of pregnant women”; it is actively involved in the development of the egg and its placement in the uterus. In addition, progesterone affects the nervous system, sebaceous and mammary glands.
When its level decreases in the second half of the menstrual cycle, the woman experiences some discomfort: pain in the lower abdomen and in the mammary glands, irritability, tearfulness, and sometimes depression may appear.
When progesterone levels are low, there is a lack of ovulation. Long delays and problems with conception and pregnancy may occur. An increase in progesterone can provoke the formation of a corpus luteum cyst and menstrual irregularities. This hormone is studied on days 19-21 of the menstrual cycle. It is recommended to conduct the study on an empty stomach.
Testosterone– male sex hormone, produced by the ovaries and adrenal glands in women. A decrease in testosterone levels can cause menstrual irregularities, excessive sweating and oily skin. When there is an excess of it, purely masculine characteristics appear: hair on the face and chest, a decrease in the timbre of the voice. Women with increased testosterone usually have a male build: average height, narrow pelvis, broad shoulders.
Exceeding the level of this hormone is dangerous for pregnant women, as it can cause early miscarriage. The maximum concentration of testosterone is determined in the luteal phase and during the period of ovulation, that is, in the first half of the menstrual cycle. The study is recommended to be carried out on days 3-7 of the menstrual cycle, on an empty stomach.
Hormone prolactin secreted by the pituitary gland. It ensures the growth and enlargement of the mammary glands, milk production during breastfeeding. Prolactin levels experience a clear periodic change during the day: an increase at night (associated with sleep) and a subsequent decrease. An increase in prolactin is also observed during a number of physiological conditions, for example, eating, muscle tension, stress, sexual intercourse, pregnancy, postpartum period, breast stimulation. To determine the level of this hormone, it is important to do an analysis in the follicular (2-6 days of the cycle) and luteal phase of the menstrual cycle (21 days of the cycle) strictly on an empty stomach and only in the morning. Immediately before taking blood, the patient should be at rest for about 30 minutes, since prolactin is a stress hormone: anxiety or even slight physical activity can affect its level.
During the luteal phase, prolactin levels are higher than during the follicular phase. Increased level The hormone prolactin can cause pain in the mammary glands before and during menstruation and even the development of mastopathy. A pathological increase in this hormone blocks ovulation, and thereby interferes with conception.
Androgenic hormones- predominantly male hormones, but are also produced in small quantities in women, responsible for libido and the development of bone and muscle tissue, the maturation of follicles in the ovarian glands. With an increase in the concentration of androgenic hormones, ovarian dysfunction and infertility often occur, increased hair growth on a woman’s body, “male-type” hair growth, and a decrease in the timbre of the voice are observed. With androgen deficiency in the female body, vitality decreases.
All androgenic hormones are released on days 2-8 of the menstrual cycle. The study is carried out on an empty stomach.
It is also necessary to remember that in addition to reproductive hormones, other hormones also take part in the regulation of the menstrual cycle, because in the body there is a functional interdependence between many endocrine glands. These connections are especially pronounced between the pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenal glands and thyroid gland. In women with severe hypo- and hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, menstrual function is impaired, and sometimes the menstrual cycle is completely suppressed.
The thyroid gland produces two important hormones Thyroxine (T4) And Triiodityronine (T3). These hormones regulate metabolic processes, carbohydrates, proteins, mental and sexual function. But the intensity of the production of these hormones is regulated by the hormone Thyroid stimulating (TSH), which, like sex hormones, is produced by the pituitary gland. Changes in its concentration are a marker of thyroid diseases.
If there are disturbances in the concentration of thyroid hormones, the woman becomes irritable, whiny, and quickly gets tired. Deviations in thyroid hormone levels are extremely dangerous for pregnant and lactating women.
Diagnosis of thyroid diseases is carried out on an empty stomach. 2-3 days before collecting blood for analysis, it is recommended to stop taking iodine-containing drugs and 1 month - thyroid hormones (except on special instructions from the treating endocrinologist), as well as limit physical activity and psycho-emotional stress on the eve of the study.
All these hormones influence...
Typically, women remember about hormones only once a month - during “critical days”, when there are mood swings, increased appetite and other unpleasant symptoms. But hormones control almost all aspects of our body’s activity, so even small imbalances affect the entire body. The acuity of thinking and the physical ability of the body to cope with diverse loads on the body depend on them. They influence height and physique, hair color and voice timbre. They control behavior and sexual desire. Very strong impact on the psycho emotional condition(mood variability, tendency to stress). Insufficient and excessive production of these substances can cause various pathological conditions, since they regulate the function of all cells in the body.The causes of hormonal imbalance can be different: from the presence of serious diseases of organs and systems to the influence of external factors. Such external factors consider stress, chronic fatigue, frequent shifts climatic zones etc. Quite often, hormonal disorders are provoked by irrational use of hormonal drugs.
Diseases that can be a consequence and cause of the development of hormonal imbalance: uterine fibroids, atherosclerosis, polycystic ovary syndrome, fibrocystic formations in the mammary gland, migraines, early menopause.
If we talk about young women, hormonal imbalance is, as a rule, a disruption of the body’s functioning, and it must be treated. Quite often, hormonal imbalance occurs after childbirth and in most cases these deviations return to normal without additional intervention. But hormonal imbalance after an abortion requires special attention; its consequences can be the most unpredictable.
A special category is women over forty years old, when disturbances in the cyclic production of hormones are caused by the approach of physiological menopause. During this period, the formation of eggs gradually stops, and the concentration of the hormone estrogen decreases significantly. Typically, these deviations are manifested by night sweats, irritability, severe fatigue, and hot flashes. This condition is well compensated by hormone replacement therapy, against which clinical manifestations are minimized. In this case, the hormonal imbalance itself is caused by natural factors, so it cannot be cured.
The human body is a complex system that performs a huge number of operations. Hormones play a significant role in the proper organization of the human body. These are catalysts for biochemical processes that are produced by the endocrine glands. Exist different types hormones, and each of them performs a specific function.
Classification of hormones
Depending on the chemical structure, these types of hormones are distinguished. The protein-peptide group combines the secretions of glands such as the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, pancreatic and parathyroid hormones. TO this type also includes calcitonin, which is produced by the thyroid gland. The second group includes derivatives of amino acids (norepinephrine and adrenaline, thyroxine, etc.). There are also steroid types of hormones. They are synthesized mainly in the gonads, as well as the adrenal glands (estrogen, progesterone). The hormones of the first two groups are primarily responsible for metabolic processes in our body. Steroid hormones control physical development and the process of reproduction. Depending on the method of signal transmission from the secretion to the cells, lipophilic and hydrophilic hormones are distinguished. The former easily penetrate the cell membrane into its nucleus. The latter bind to receptors on the surface of the structural element, triggering the synthesis of so-called intermediary molecules. It is typical that hydrophilic hormones are transported through the bloodstream, while lipophilic hormones bind to its proteins and are transported that way.
Human endocrine system
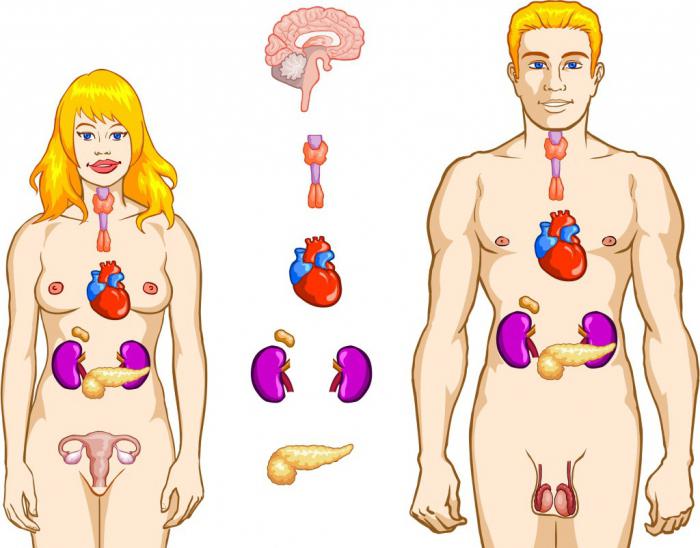
This is the name given to the totality of all glands and organs in the human body that secrete special biologically active elements - hormones. The endocrine system is responsible for many processes, while ensuring the normal development of the body. She's in control chemical reactions, generates energy, affects the psycho-emotional state of a person. The endocrine system includes the thyroid, parathyroid, pancreas, pituitary and pineal glands, adrenal glands, and hypothalamus. This also includes organs such as testicles and ovaries. All hormones enter directly into the blood or lymph. Any disturbances in the functioning of the human endocrine system can cause serious diseases (diabetes mellitus, tumor processes, obesity, hyper- and hypothyroidism
). 
Tissue hormones, their types and functions
This type of hormone is produced in the tissues of the body and their effect is usually local. Sometimes such hormones can enter the blood. Histamine is a substance that plays a large role in the occurrence of allergic reactions. In the active state, it causes dilation of blood vessels and increases their permeability. Histamine also promotes contractions of the intestinal muscles and can cause spasms in the bronchi. Serotonin has the following effect: blood vessels narrow, their permeability decreases. It is also called the hormone of happiness. If its production is normal, a person has good mood, he feels a surge of strength. Both histamine and serotonin are actively involved in the transmission of impulses to the brain. Kinins are another tissue hormone. Their types and functions are as follows. Nanopeptide, kallidin, T-kinin, bradykinin (reduces blood pressure) - all of them, when they enter the blood, cause symptoms of the inflammatory process. These hormones are involved in the regulation of blood circulation. Another category of biologically active tissue secretions is prostaglandins. They affect the smooth muscles of organs and reduce the secretion of gastric juice. Substances such as kelons control cell division. Another type of tissue hormones is gastrin, secretin.
Thyroid. Types of hormones and their functions
This organ has the shape of a butterfly and is located in the neck (front). Its weight is relatively small - about 20 grams. Regulation of sexual (reproductive) functions digestive systems, metabolic processes, maintaining a normal psycho-emotional state - all this is controlled by thyroid hormones. Their types are as follows. Thyroxine, triiodothyronine - extremely important secrets for human health. In order for them to form, a sufficient intake of iodine into the body is necessary. The action of these hormones is similar, but triiodothyronine is more active. First of all, these substances take part in energy metabolic processes. They also affect the functioning of the heart muscle, intestines, central nervous system. Also, these types of hormones take part in the development of the entire organism and the maturation of the reproductive system. Calcitonin is responsible for the level of calcium in the blood and also takes part in water and electrolyte metabolism. Insufficient production leads to rapid human fatigue, lethargy, and all metabolic processes slow down. If they are produced in excess, then excessive activity and excitability can be observed. 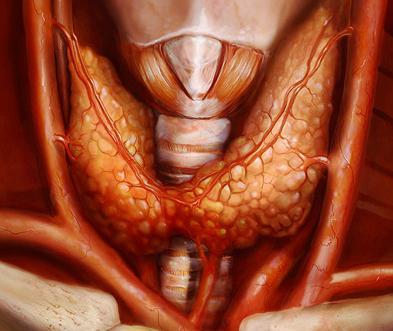
Analysis of hormones produced by the thyroid gland
If a person experiences changes such as weight fluctuations (sudden weight gain or loss), problems with sexual desire, cessation of menstruation, developmental delay (psychological) in children, then a blood test for hormones produced by the thyroid gland is required. To pass it, you must prepare in a special way. It is best to limit any physical activity the night before the test. It is also worth eliminating alcohol, coffee, tobacco (at least 24 hours before). Blood sampling occurs in the morning, on an empty stomach. Thyroid hormones can be either bound or free. Therefore, during the studies, the amount of free thyroxine, free triiodothyronine, thyrotropin, as well as the level of antibodies to thyroid peroxidase and thyroglobulin are determined. Typically, the study takes one day. Depending on the results obtained, we can talk about one or another disease. 
and her secrets
On the posterior surface of the thyroid gland there are small glands, which are also called parathyroid glands. They are directly involved in the exchange of calcium and phosphorus in the body. Depending on the characteristics of the person, the gland can be of a reticular type, alveolar, or in the form of a solid mass. It synthesizes parathyroid hormone, which, like calcitonin, takes part in calcium metabolism. It also affects the skeletal system, intestines, and kidneys. If the production of parathyroid hormone is impaired, then mental disorders, bone problems, calcification of internal organs and blood vessels are possible. With hypoparateriosis, muscle cramps appear, the heart rate increases, and headaches may occur. If these signs are present, a blood test for parathyroid hormones may be needed. Their high content increases the level of calcium in the blood, and as a result, causes fragility of bone tissue.
Hormones produced by the adrenal glands
The adrenal glands are paired organs that are located on top of the kidneys. These types of hormones and their functions are as follows. The cortical layer of the glands produces substances that regulate the exchange of nutrients and minerals. Hormones of this type also control glucose levels. The adrenal medulla synthesizes adrenaline and norepinephrine. They are often produced during strong emotional outbursts (fear, danger). When these hormones enter the blood, it increases arterial pressure, the heart rate increases, the excitability of the receptors of the organs of vision and hearing increases. Thus, the body prepares for the need to endure a stressful situation. The adrenal glands produce glucocorticoid hormones (cortisol), which regulate carbohydrate metabolism. Their concentration depends on the time of day: maximum amount cortisol levels occur at approximately 6 a.m. Mineralocorticoid hormones (aldosterone) regulate salt metabolism. Thanks to them, fluid is retained in the body. The adrenal glands also secrete androgens such as androstenedione and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). They regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands and form libido. A blood test for adrenal hormones examines the level of DHEA. Its high content may indicate the presence of gland tumors. In addition, an excess of this hormone leads to serious consequences during pregnancy (miscarriage, malnutrition of the child, problems with the placenta). If there are complaints about increased hair growth, early puberty, menstrual irregularities, muscle weakness, a blood test for cortisol may be needed. 
Pancreas. Types of hormones and their functions
In addition to taking an active part in the digestive process, it also produces hormones that are essential for the normal functioning of the body. All of them enter directly into the human blood. This organ produces the following types of hormones: insulin, c-peptide, glucagon. The main function of insulin is to regulate sugar levels. If the processes of its synthesis are disrupted, the development of diabetes mellitus. Insulin also affects the production of active substances in the gastrointestinal tract and the synthesis of estrogen. It can be found in the body in free and bound form. If the amount of insulin is insufficient, the process of converting glucose into fat and glycogen is disrupted. At the same time, toxins (for example, acetone) can accumulate in the body. Glucagon is also an extremely necessary element for our body. It activates the process of fat breakdown and helps increase blood glucose levels. It also helps reduce the level of calcium and phosphorus in the blood. The types of action of pancreatic hormones are closely interrelated. Their combined influence ensures optimal glucose levels.
Functions of pituitary hormones
The pituitary gland is an endocrine gland, which consists of an anterior and posterior lobe, as well as small area between them. This organ weighs only 0.5 grams, but performs quite important functions. The pituitary gland synthesizes the following types of human hormones. Adrenocorticotropic hubbub stimulates the adrenal cortex. It also affects the formation of melanin. affects the proper functioning of the reproductive system. Thanks to it, ovulation is stimulated and androgens are produced. Thyroid-stimulating hormone coordinates the secretion of biologically active substances of the thyroid gland. Somatotropin takes an active part in the growth of the body and protein synthesis. It can also affect glucose levels and lipid breakdown. This hormone is responsible for the normal physical development of the human body. Increasing its level leads to gigantism. If somatotropin is below normal (in children), then short stature is observed. By the way, different types of growth hormone (synthetic) are used in the fight against dwarfism and to increase weight in athletes. Prolactin is the main hormone responsible for milk production in women. Also, thanks to its production during breastfeeding, another pregnancy does not occur. Melanotropin is produced in the middle lobe. The posterior lobe produces types of human hormones such as oxytocin and vasopressin. The first promotes contraction of the uterus, colostrum is produced. Vasopressin stimulates the muscles of organs such as the intestines, uterus, and blood vessels. 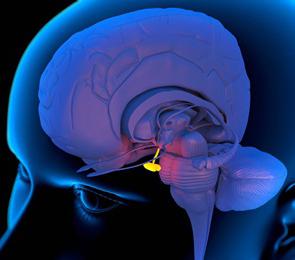
Sex glands
The ovaries and testes produce sex hormones. Their types are as follows. First of all, they are divided into women's and men's. However, they can also be present in small quantities in the opposite sex. Types of testosterone, androsterone, dihydrotestosterone, androstenediol. All of them ensure the development of both primary and secondary sexual characteristics. It should be noted that their level does not tolerate such fluctuations in comparison with women's secretions. Thanks to testosterone, seminal fluid is produced and desire for sex is stimulated. opposite sex. The muscles and skeleton also develop in a special way, and a characteristic male timbre of voice appears. Other types of steroid hormones (in particular, dihydrotestosterone) provide male behavior, as well as a characteristic appearance: hair growth in certain areas, body structure. The types of female hormones are: progesterone, estrogen, prolactin (produced by the pituitary gland).
Progesterone is produced by the corpus luteum. This gland is formed after ovulation. Performs the following functions: promotes the growth of the uterus, provides the opportunity for the egg (fertilized) to attach to its cavity. Progesterone prepares a woman for pregnancy and also contributes to bearing a child. If the amount of hormone is insufficient, the menstrual cycle will be disrupted and bleeding may occur. Affects low level progesterone and, as a rule, a woman suffers from sudden mood swings. An increased level of the hormone may indicate either pregnancy or a tumor process. Estrogens - special types hormones in women. These include estradiol, estrone, estriol. These substances are responsible for the formation female type figures, increase skin tone and elasticity. In addition to the appearance, they contribute to the normal course of menstruation. They also protect blood vessels from the accumulation of lipid plaques, promote the growth of bone tissue, and retain calcium and phosphorus in it. If the level of estrogen is insufficient, male type hair growth is observed, the skin ages earlier, accumulates excess weight in the abdomen, hips, and bones become more fragile. 
Blood test for sex hormones
Types of hormone tests include blood testing to determine whether it contains sexual secretions. It is prescribed if the following disorders occur: problems with the menstrual cycle, inability to conceive a child, miscarriage, etc. For men, such an analysis is indicated in cases of suspected tumor processes or infertility. Blood must be donated in the morning; you cannot eat beforehand. The day before, you should give up tobacco, alcohol, and heavy physical activity. A woman needs to choose the right time to take the test, since hormone levels depend on the day of the menstrual cycle. Several indicators are examined simultaneously. The content in the maximum number indicates the onset of ovulation. In men, this hormone promotes the growth of the seminiferous tubules and affects the concentration of testosterone. When diagnosing infertility, special attention is paid to luteinizing hormone. In women, it is responsible for follicle maturation, ovulation, and the formation of a gland such as the corpus luteum. If it is impossible to get pregnant, the indicators of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone in combination are examined. A blood test is also performed to determine the presence of a certain amount of prolactin. If there are deviations from the norm, the onset of ovulation becomes more difficult. The blood is also tested for testosterone. It is present in the body of both sexes. If its levels are lower than normal in men, then the quality of sperm deteriorates. It also negatively affects potency. In women, excess testosterone can cause miscarriage.
Some people try to eliminate problems in the functioning of the body on their own, without resorting to the help of doctors. However, such self-medication can negatively affect future health. After all, a disruption in the functioning of one or another organ occurs in the process of insufficient or excessive production of hormones.
However, every person has heard about these substances since childhood. Meanwhile, scientists continue to study the structure of these substances and the functions they perform. What are hormones, why do people need them, what types of hormones exist, and what effect do they have on him?
What are hormones
Hormones are biologically active substances. Their production occurs in specialized cells of the endocrine glands. Translated from ancient Greek, the word “hormones” means “to stimulate” or “to excite.”
It is this action that is their main function: when produced in some cells, these substances induce cells of other organs to act, sending them signals. That is, in the human body, hormones play the role of a unique mechanism that triggers all vital processes that cannot exist separately.
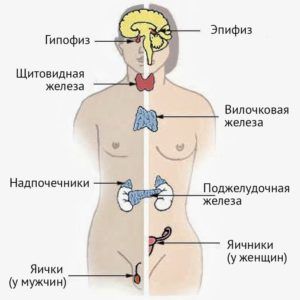
To understand their significance, it is necessary to understand where they are formed. The main sources of hormone production are the following internal glands:
- pituitary;
- thyroid and parathyroid glands;
- adrenal glands;
- pancreas;
- testes in men and ovaries in women.

Some may also participate in the formation of these substances. internal organs, which include:
- liver;
- kidneys;
- placenta during pregnancy;
- the pineal gland, located in the brain;
- gastrointestinal tract;
- the thymus or thymus gland, which actively develops before puberty and decreases in size with age.
The hypothalamus is a small part of the brain that coordinates the production of hormones.
How do hormones work?
Once you understand what hormones are, you can begin to study how they work.
Each hormone affects specific organs, called target organs. Moreover, each hormone has its own chemical formula, which determines which organ will become the target. It is worth noting that the target may be not one organ, but several.
Unlike the nervous system, which transmits impulses through nerves, hormones enter the blood. They act on target organs through cells equipped with special receptors that can perceive only certain hormones. Their relationship is like a lock with a key, where the receptor cell acts as the lock, which is opened by the hormone key.
By attaching to receptors, hormones penetrate into internal organs, where, using chemical action, they force them to perform certain functions.
Active study of hormones and the glands that produce them began in 1855. During this period, the English doctor T. Addison first described bronze disease, which develops as a result of dysfunction of the adrenal glands.
Other doctors also showed interest in this science, for example, C. Bernard from France, who studied the processes of formation and release of secretion into the blood. The subject of his study was also the organs that secreted them.
And the French doctor C. Brown-Séquard managed to find a relationship between various diseases and decreased function of the endocrine glands. It was he who first proved that many diseases can be cured with the help of remedies prepared from gland extracts.

In 1899, English scientists managed to discover the hormone secretin, produced by the duodenum. A little later they gave it the name hormone, which marked the beginning of modern endocrinology.
Until now, scientists have not been able to study everything about hormones, while continuing to make new discoveries.
Types of hormones
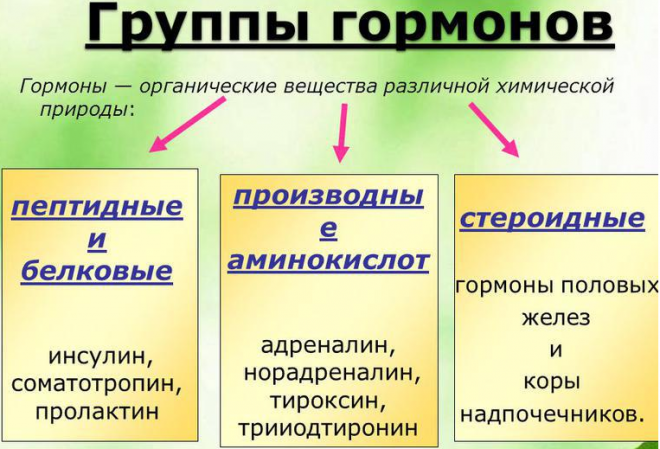
Hormones come in several types, distinguished by their chemical composition.
- Steroids. These hormones are produced in the testicles and ovaries from cholesterol. These substances perform the most important functions that allow a person to develop and acquire the necessary physical form that adorns the body, as well as to reproduce offspring. Steroids include progesterone, androgen, estradiol and dihydrotestosterone.
- Fatty acid derivatives. These substances act on cells located near those organs that are involved in their production. These hormones include leukotrienes, thromboxanes and prostaglandins.
- Amino acid derivatives. These hormones are produced by several glands, including the adrenal glands and the thyroid gland. And the basis for their production is tyrosine. Representatives of this type are adrenaline, norepinephrine, melatonin, and thyroxine.
- Peptides. These hormones are responsible for carrying out metabolic processes in the body. And the most important component for their production is protein. Peptides include insulin and glucagon, produced by the pancreas, and growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland.
The role of hormones in the human body
All life path The human body produces hormones. They influence any processes that happen to a person.
- Thanks to these substances, each person has a certain height and weight.
- Hormones influence a person's emotional state.
- Throughout life, hormones stimulate the natural process of cell growth and breakdown.
- They participate in the formation of the immune system, stimulating or inhibiting it.
- Substances produced by the endocrine glands control metabolic processes in the body.
- Under the influence of hormones, the body can more easily tolerate physical activity and stressful situations. For these purposes, the active hormone adrenaline is produced.
- With the assistance of biologically active substances, preparation for a certain life stage, including puberty and childbirth.
- Certain substances control the reproductive cycle.
- A person also experiences feelings of hunger and satiety under the influence of hormones.
- With normal production of hormones and their function, sexual desire increases, and with a decrease in their concentration in the blood, libido decreases.
The main human hormones ensure the stability of the body throughout life.
The influence of hormones on the human body
Under the influence of certain factors, the stability of the process may be disrupted. A sample list of them looks like this:
- age-related changes in the body;
- various diseases;
- stressful situations;
- changes in climatic conditions;
- unfavorable environmental situation.
In the body of men, the production of hormones is more stable than in women. In the female body, the amount of hormones secreted varies depending on various factors, including the phase of the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, childbirth and menopause.
The following signs indicate that a hormonal imbalance may have occurred:
- general weakness of the body;
- cramps in the limbs;
- headache and ringing in the ears;
- sweating;
- impaired coordination of movements and slow reaction;
- memory impairment and lapses;
- sudden changes in mood and depression;
- unreasonable decrease or increase in body weight;
- stretch marks on the skin;
- disruption of the digestive system;
- hair growth in places where it should not be;
- gigantism and nanism, as well as acromegaly;
- skin problems, including increased oily hair, acne and dandruff;
- menstrual irregularities.
How are hormone levels determined?
If any of these conditions manifest themselves systematically, you should consult an endocrinologist. Only a doctor, based on an analysis, will be able to determine which hormones are produced in insufficient or excessive quantities and prescribe adequate treatment. In this case, determining the level of all possible hormones is not required, since an experienced doctor will determine the type of research required based on the patient’s complaints.
Why is a blood test prescribed for hormone levels? It is necessary to confirm or exclude any diagnosis.
If necessary, tests are prescribed that determine the concentration in the blood of hormones secreted by the following endocrine glands:
- pituitary gland;
- thyroid gland;
- adrenal glands;
- testes in men and ovaries in women.
As an additional examination, women may be prescribed prenatal diagnostics to identify pathologies in fetal development. early stages pregnancy.

The most popular blood test is basal level determination. certain type hormone. This examination is carried out in the morning on an empty stomach. But the level of most substances tends to change throughout the day. As an example, somatotropin is a hormone that stimulates growth. Therefore, its concentration is studied throughout the day.
If a study is carried out on the hormones of the endocrine glands that depend on the pituitary gland, an analysis is carried out to determine the level of the hormone produced by the endocrine gland and the pituitary hormone that causes this gland to produce it.

How to achieve hormonal balance
For mild hormonal imbalances, lifestyle adjustments are indicated:
- Maintaining a daily routine. Full functioning of the body's systems is possible only by creating a balance between work and rest. For example, the production of somatotropin increases 1-3 hours after falling asleep. In this case, it is recommended to go to bed no later than 23 hours, and the duration of sleep should be at least 7 hours.
- Physical activity allows you to stimulate the production of biologically active substances. Therefore, 2-3 times a week you need to do dancing, aerobics, or increase your activity in other ways.
- A balanced diet with increased protein intake and decreased fat intake.
- Compliance with drinking regime. During the day you need to drink 2-2.5 liters of water.
If more intensive treatment is required, a table of hormones is studied, and medications that contain their synthetic analogs are used. However, only a specialist has the right to prescribe them.


